India Approves Supernova Stent Retriever: India has taken a significant leap in its battle against stroke-related deaths and disabilities. The country’s medical regulator has approved the Supernova stent retriever, a state-of-the-art device designed to remove blood clots from the brain during ischemic strokes. This development marks the beginning of a new era in advanced neurology, bringing cutting-edge treatment closer to millions of patients who were earlier deprived of timely and effective intervention.
The approval follows the successful GRASSROOT clinical trial, conducted across 16 of India’s top hospitals, including AIIMS Delhi, JIPMER Puducherry, and CMRI Kolkata. The stent’s primary function is to swiftly restore blood flow by capturing and removing clots, giving patients a much higher chance of survival and recovery without long-term disability.
More importantly, the device will be manufactured domestically, cutting its cost nearly in half—from around ₹3.5 lakh to ₹1.75 lakh—making it far more affordable for Indian families.
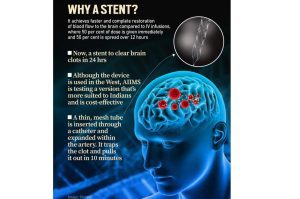
India Approves Supernova Stent Retriever: How the Device Works
The Supernova stent retriever is used in a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy, considered the gold standard for ischemic stroke treatment worldwide.
- A catheter is inserted through an artery, usually in the groin.
- The stent, shaped like a tiny mesh tube, is guided into the blocked blood vessel in the brain.
- Once inside, it expands to ensnare the clot.
- The clot is then carefully pulled out, instantly restoring blood circulation.
Unlike traditional clot-dissolving drugs, which can take time and are not always effective, mechanical removal offers rapid results—often within minutes. This is crucial because, in stroke treatment, “time is brain”: every passing minute without blood flow destroys millions of brain cells.
For an overview of how mechanical thrombectomy saves lives, see American Stroke Association.

Why It Matters for India
India records nearly 1.75 million ischemic strokes every year, a staggering number that places immense pressure on the healthcare system. Of these, nearly 3.75 lakh patients are eligible for thrombectomy procedures, but only about 5,000 actually receive it due to lack of access, cost, and awareness.
The Supernova retriever directly addresses these barriers:
- Affordability: Halving the price puts treatment within reach of middle-class and even some lower-income households.
- Accessibility: Trials across hospitals in both metros and tier-2 cities lay the foundation for nationwide use.
- Adaptability: The device has been customized for Indian patients, who often suffer strokes at a younger age and have smaller arterial diameters compared to Western populations.
The GRASSROOT Trial: Building Indian Evidence
The GRASSROOT trial began on August 15, 2024, symbolically launched on India’s Independence Day. This large-scale clinical study aimed to gather India-specific evidence for the device’s safety and effectiveness.
The first patient was treated at AIIMS Delhi the very same day, successfully undergoing thrombectomy with promising results. Over the following months, hospitals across the country reported similar outcomes, which formed the scientific basis for regulatory approval.
This trial is not only significant for stroke care—it also reflects India’s growing ability to conduct world-class clinical research and develop medical technologies tailored to its own population.
For more details on thrombectomy trials and their global impact, you can explore National Library of Medicine – Mechanical Thrombectomy Overview.
Domestic Innovation: Toward Self-Reliance
India has long depended on imported devices for advanced neurological treatments. The Supernova marks a shift, as it is produced by Gravity Medical Technology with a vision to make world-class treatment accessible at Indian prices.
Parallelly, S3V Vascular Technologies, a homegrown medtech firm, is setting up manufacturing units in Tamil Nadu to produce indigenous mechanical thrombectomy devices. This initiative, backed by government support, could soon make India not only self-reliant but also a global exporter of affordable stroke care tools.
This fits into India’s broader healthcare strategy under the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (self-reliant India) initiative, where domestic production of critical medical devices reduces dependency on costly imports.
For more on how medical device innovation shapes stroke treatment worldwide, refer to World Stroke Organization.
Challenges Ahead
While the approval is a breakthrough, several challenges remain:
- Awareness Gap: Many patients and even general practitioners are unaware of thrombectomy as an option.
- Infrastructure: Only select hospitals have the facilities and trained neuro-interventionists to perform such procedures.
- Time Sensitivity: Stroke treatment requires action within a “golden window” of 4–6 hours. Reaching a qualified hospital in time is still a challenge for rural and semi-urban populations.
- Training Needs: Thousands of doctors and paramedics need specialized training to ensure wide-scale adoption.
Global Comparisons and India’s Place
Stent retrievers are already standard in developed countries. Devices like MERCI Retriever in the U.S. and Embotrap II in Europe have been saving lives for years. Now, with the Supernova, India joins the league of nations offering cutting-edge, cost-effective stroke solutions tailored to its own demographic needs.
To learn more about early stent retriever technology, see MERCI Retriever – Wikipedia.
Looking Ahead
Experts believe the approval of the Supernova retriever could reduce India’s stroke-related disability rates dramatically. If coupled with national stroke awareness campaigns, expanded hospital infrastructure, and telemedicine-based early diagnosis, it has the potential to save hundreds of thousands of lives each year.
Furthermore, with domestic production and scaling, India could become a hub for affordable stroke devices, supplying not just its own population but also developing nations in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Conclusion
The approval of the Supernova stent retriever is more than just a medical milestone—it is a symbol of India’s advancing healthcare capabilities. By combining clinical innovation, affordability, and accessibility, the device represents hope for millions of families who once saw stroke as a near-certain sentence of disability or death.
If properly implemented, this breakthrough could transform stroke care in India, set a precedent for future medical device innovation, and reaffirm India’s place in the global healthcare ecosystem.
🔗 External Resources for Further Reading:
- American Stroke Association – Mechanical Thrombectomy
- World Stroke Organization
- National Library of Medicine – Mechanical Thrombectomy Overview
- MERCI Retriever – First Stent Device for Stroke
Also read: Home | Channel 6 Network – Latest News, Breaking Updates: Politics, Business, Tech & More

